Leave Your Message
Busbar insulators are critical components in electrical distribution systems, ensuring safe and reliable operation by preventing short circuits and maintaining system integrity. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the global market for electrical insulation products, including busbar insulators, was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% through 2027. The increasing demand for energy-efficient power distribution systems, driven by urbanization and industrial expansion, further underscores the importance of busbar insulators in managing high current loads and minimizing energy loss. With the rise of renewable energy sources and smart grid technology, the role of busbar insulators is becoming even more vital in securing safety and performance in modern electrical infrastructures. Therefore, understanding the various types and specifications of busbar insulators is essential for engineers and designers aiming to enhance the reliability of electrical distribution networks.
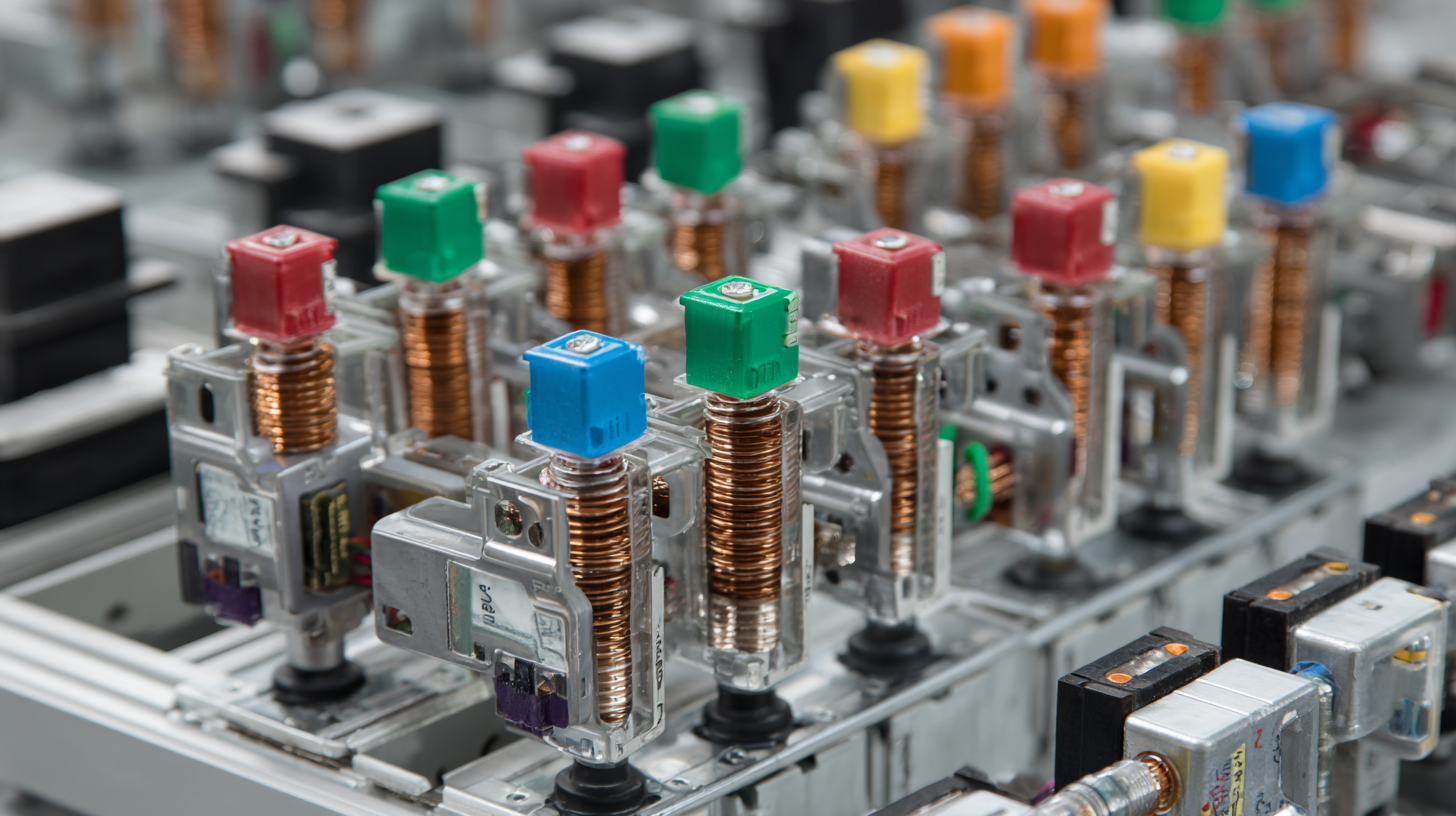
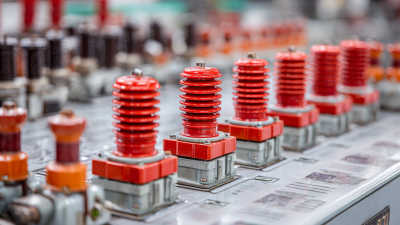
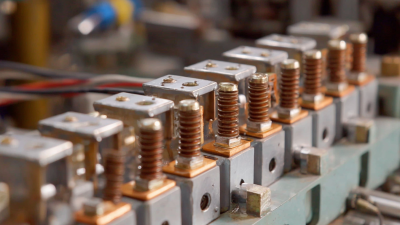
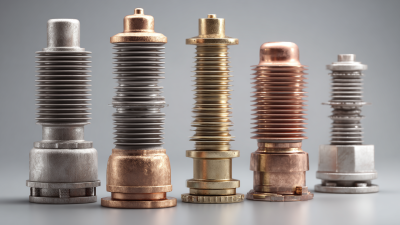
Busbar insulators play a critical role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical distribution systems. Identifying different types of busbar insulators is essential for maintenance and system optimization. The most common types include porcelain, glass, and polymer insulators, each with distinct characteristics suited for specific applications.
Porcelain insulators are known for their durability and weather resistance. They provide excellent electrical insulation and are often used in outdoor applications. On the other hand, glass insulators offer transparency, which allows for easy visual inspection. They are adept at handling high voltage and are often used in environments where the potential for mechanical damage is a concern. Lastly, polymer insulators, made from advanced composite materials, are lightweight and resistant to vandalism and extreme weather, making them increasingly popular in modern installations. Understanding these differences enables engineers and technicians to select the appropriate insulators for their specific needs, ensuring reliable electric distribution and minimizing the risk of failures.
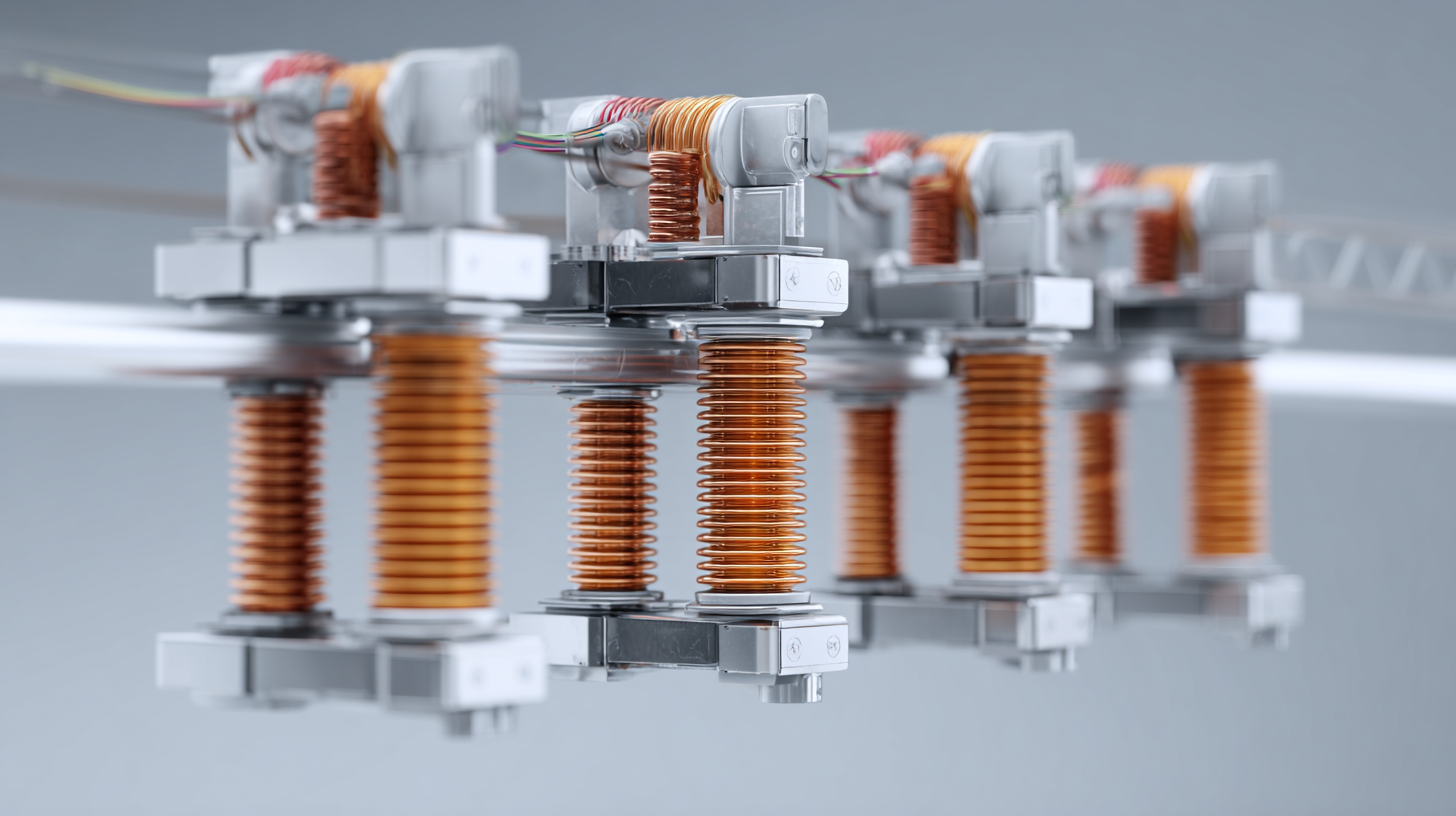
Busbar insulators play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical distribution systems. Assessing the mechanical strength of these insulators is paramount, as it determines their reliability under various operational conditions. Industry standards, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), highlight that busbar insulators must withstand significant mechanical stresses without failure. For instance, IEC 61140 mandates that insulators should endure impacts of up to 25 Joules, which translates to testing their resistance to both tension and shear forces.
Recent studies emphasize the importance of material selection and design in enhancing mechanical strength. Advanced composite materials, like epoxy resins reinforced with glass fibers, have shown improved characteristics, achieving up to 40% greater tensile strength compared to traditional ceramic insulators. Additionally, a report by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) suggests that regular monitoring of environmental conditions and mechanical wear can further optimize the performance and longevity of busbar insulators. Rigorous testing protocols and adherence to safety standards ensure that these essential components continue to support the integrity of electrical distribution networks.
Proper installation of busbar insulators is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficiency of electrical distribution systems. The first step in ensuring effective installation is to thoroughly assess the environmental conditions where the busbars will be placed. Factors such as humidity, temperature variations, and exposure to contaminants can significantly influence the performance of insulators. Selecting the right materials and designs based on these conditions will enhance the reliability of the electrical system.
Once the appropriate insulators are chosen, meticulous installation procedures must be followed. This includes ensuring that all surfaces are clean and free from debris before mounting the insulators to prevent any faults. Furthermore, correct alignment and secure fastening of the insulators are essential to avoid mechanical stress that could lead to failure. Regular inspections during and after installation can help identify potential issues early on, safeguarding against costly repairs and ensuring that the entire electrical distribution system operates smoothly and safely.
Maintaining and inspecting busbar insulators is crucial for ensuring their longevity and the overall safety of electrical distribution systems. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for any signs of wear, damage, or contamination. This includes examining the surfaces for cracks, chips, or discoloration, which can indicate deterioration or electrical stress. It's essential to assess the physical integrity of these insulators to prevent potential failures that could lead to system outages or hazardous situations.
In addition to visual inspections, periodic cleaning is vital to remove dust, dirt, or any other contaminants that could affect the performance of the insulators. Using appropriate cleaning agents and methods is important to avoid causing further damage. Furthermore, monitoring environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature, can provide insights into the potential risks for insulator degradation. By implementing a structured maintenance plan, electrical professionals can enhance the reliability of busbar insulators and extend their operational lifespan, ensuring safe electrical distribution.
This bar chart illustrates the results of a survey on the frequency of maintenance and inspection of busbar insulators across different facilities. The data reflects the importance of regular checks for ensuring the longevity and safety of electrical distribution systems.
When selecting materials for busbar insulators, it is essential to consider the specific application requirements, such as electrical performance, thermal management, and environmental durability. Recent trends in material science emphasize the role of advanced materials, such as diamond-based insulators, which have been highlighted for their excellent thermal conductivity and efficiency in heat dispersion. According to a report, diamond materials are poised to become a game-changer in managing overheating issues within semiconductor applications, a critical aspect for high-performance electrical distribution systems.
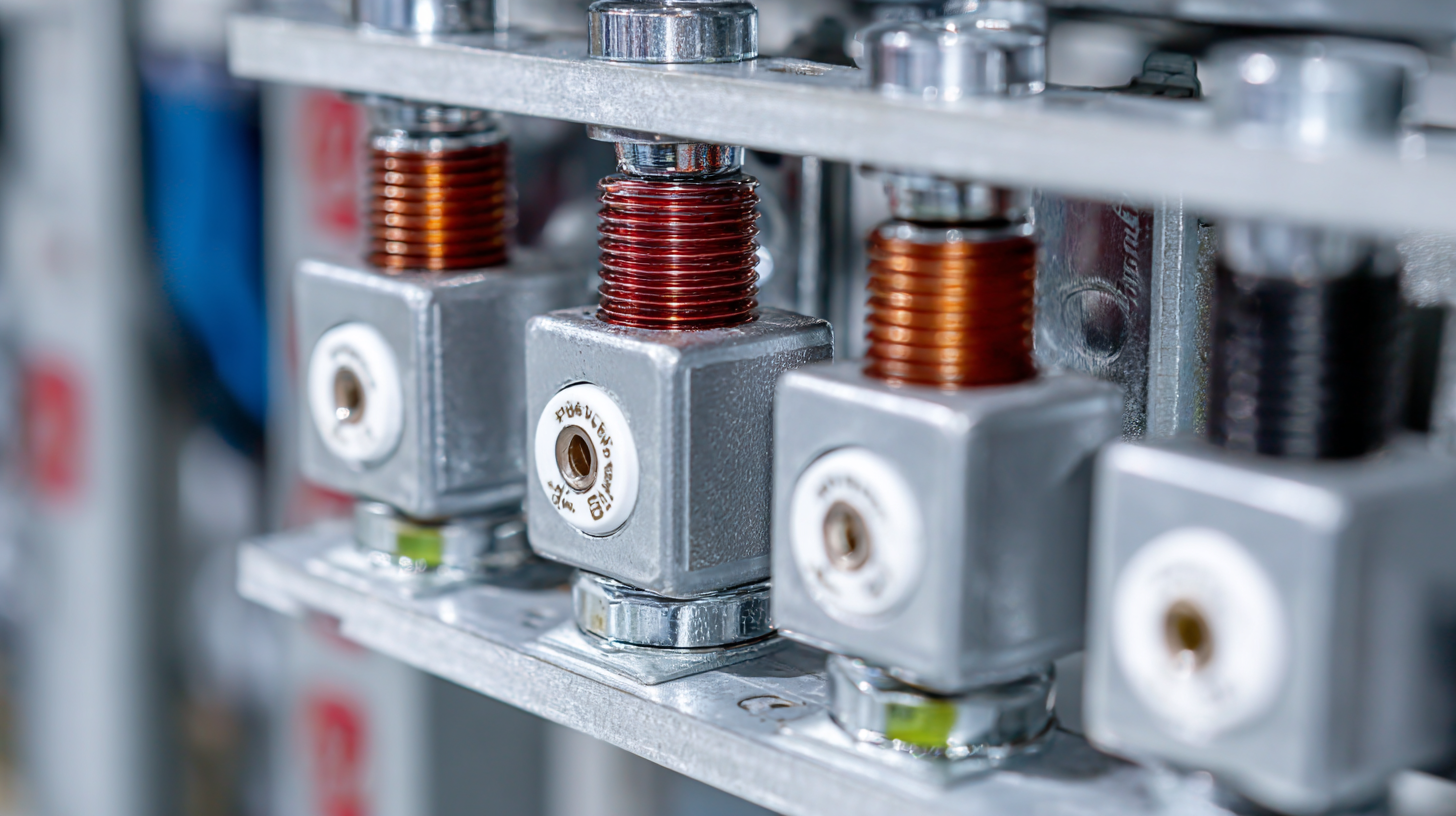
Additionally, sustainable materials are becoming increasingly important in the selection process. As companies move towards eco-friendly practices, the integration of recyclable and sustainably-sourced materials into the manufacturing of busbar insulators is gaining traction. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also supports compliance with global standards for sustainable development in the electrical industry. The combination of performance and sustainability is essential in ensuring that busbar insulators meet the evolving demands of various applications, especially in the face of increasingly stringent regulations and market expectations.