Leave Your Message
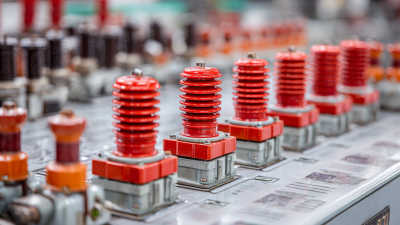
In modern electrical systems, the role of a Busbar Insulator cannot be overstated, as it is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of power distribution. With the increasing demand for electricity and the complexity of contemporary electrical grids, the need for proper insulation has become more prominent than ever.
This article aims to delve into the significance of Busbar Insulators, exploring their functionality, types, and the best practices for their implementation. By understanding the various aspects of Busbar Insulators, engineers and technicians can enhance the performance of electrical systems, safeguard against potential failures, and ultimately contribute to the seamless transmission of electrical energy.
As we navigate through the key considerations and methodologies involved in selecting and maintaining these essential components, readers will gain valuable insights into the essential role that Busbar Insulators play in the modern world of electrical engineering.
Busbar insulators play a crucial role in power distribution systems by ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical networks. These insulators serve as protective barriers that prevent electrical faults and minimize the risk of short circuits. In high-voltage environments, the effectiveness of busbar insulators becomes even more pronounced, as they help to maintain electrical isolation between conductive components. This isolation is essential for safeguarding equipment and personnel from potential hazards, as well as for optimizing the overall reliability of the power system.
Moreover, the selection of appropriate busbar insulators is vital to accommodate various environmental conditions and electrical loads. Insulators made from high-quality materials can withstand extreme temperatures and humidity levels, reducing the likelihood of degradation and failure. Additionally, advancements in insulator technology have led to the development of solutions that enhance performance while minimizing maintenance needs. As power distribution systems become increasingly complex, ensuring that busbar insulators are properly integrated and functioning effectively remains a top priority for engineers and operators alike.
| Type of Insulator | Material | Voltage Rating (kV) | Temperature Range (°C) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain Insulator | Porcelain | 36 | -40 to 120 | Power Substations |
| Polymer Insulator | Silicone Rubber | 36 | -30 to 90 | Transmission Lines |
| Glass Insulator | Glass | 110 | -40 to 160 | High Voltage Systems |
| Composite Insulator | FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymer) | 72.5 | -40 to 120 | Outdoor Installations |
| Silicone Insulator | Silicone | 36 | -50 to 200 | Renewable Energy Systems |
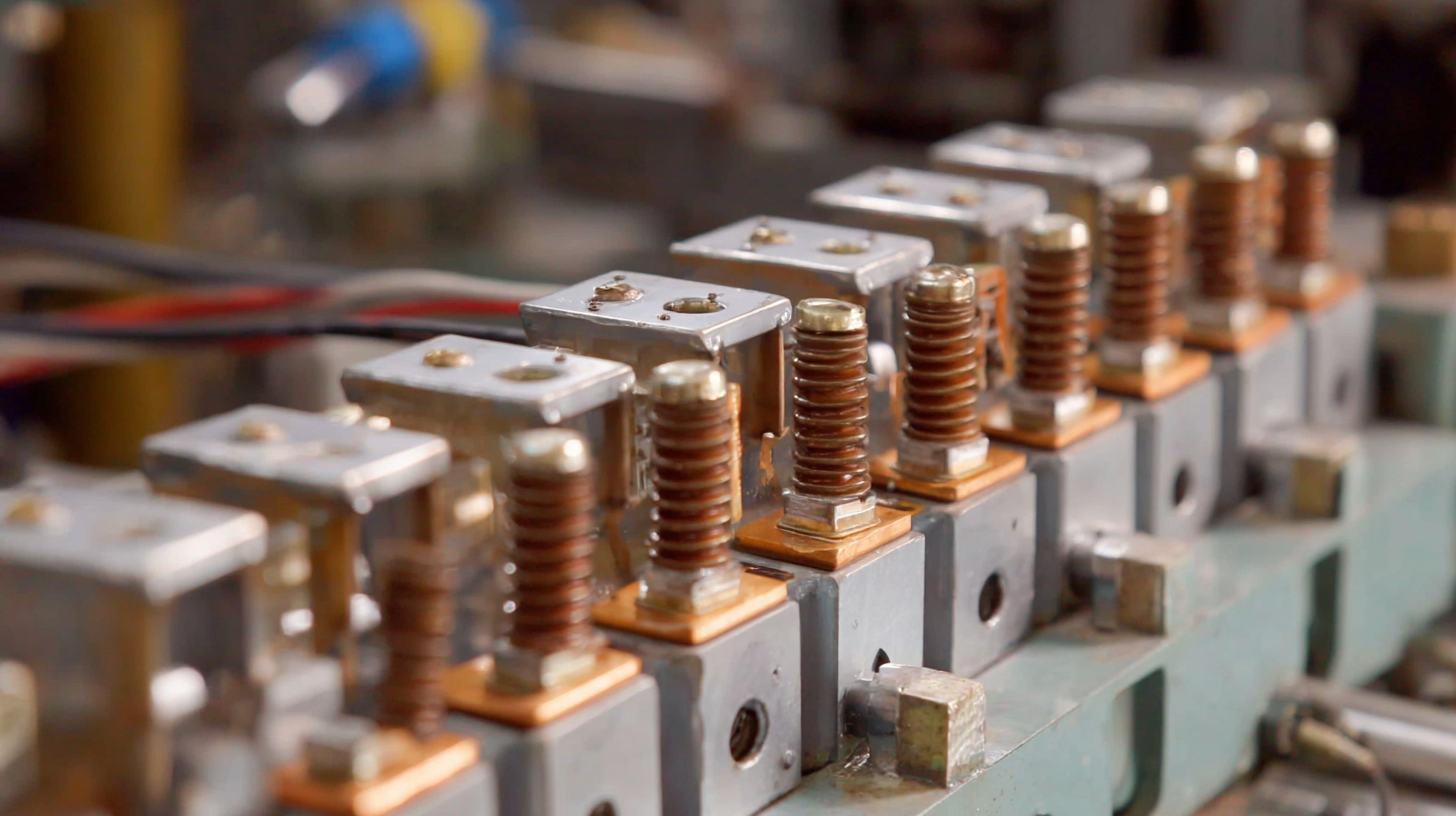
Busbar insulators play a crucial role in enhancing the safety and reliability of modern electrical systems, particularly in high-demand environments. High-quality busbar insulators are essential for preventing electrical faults and minimizing energy loss. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the effective insulation provided by these components can increase the lifespan of electrical equipment by up to 30%. This extended longevity is not only beneficial for operational efficiency but also translates into significant cost savings over time.
Moreover, the use of high-quality materials in busbar insulators improves the overall performance of electrical applications by ensuring that they can withstand extreme electrical and environmental conditions. Industry data from the IEEE indicates that systems employing advanced busbar insulators experience a reduction in maintenance costs by approximately 25%, highlighting their importance in maintaining system integrity. Additionally, robust insulation helps in achieving higher load capabilities, which is vital as electrical demands continue to grow in industrial and commercial sectors.
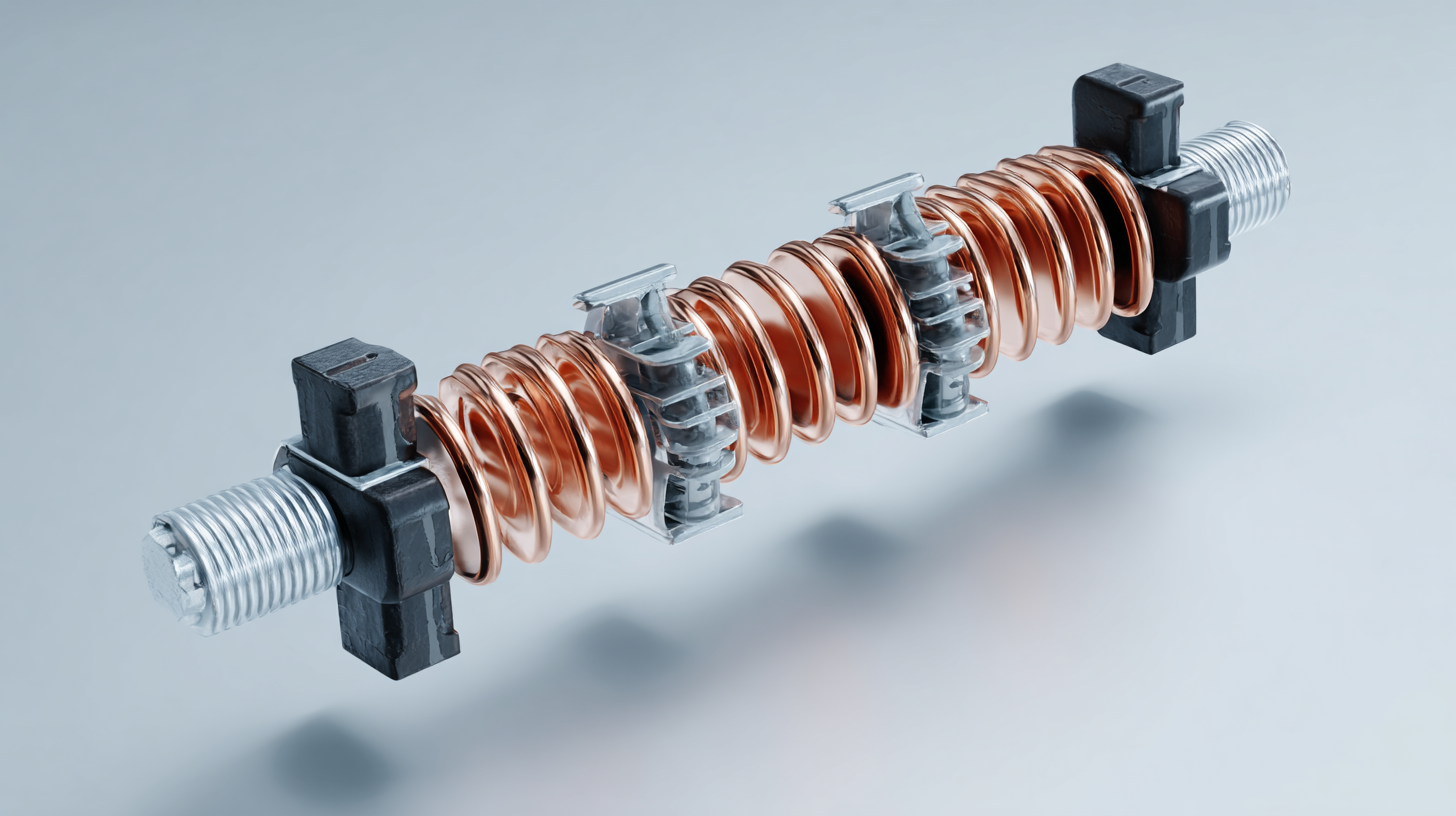 Busbar insulators play a crucial role in modern electrical systems, ensuring safe and efficient operation. Industry standards and regulatory guidelines, such as those outlined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), emphasize the necessity of high-performance insulators. According to the IEC 61109 standard, polymeric insulators must demonstrate excellent hydrophobicity and superior electrical strength to withstand varying environmental conditions. These attributes significantly contribute to the reliability of busbar systems, particularly in humid and polluted environments where electrical breakdown is a concern.
Busbar insulators play a crucial role in modern electrical systems, ensuring safe and efficient operation. Industry standards and regulatory guidelines, such as those outlined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), emphasize the necessity of high-performance insulators. According to the IEC 61109 standard, polymeric insulators must demonstrate excellent hydrophobicity and superior electrical strength to withstand varying environmental conditions. These attributes significantly contribute to the reliability of busbar systems, particularly in humid and polluted environments where electrical breakdown is a concern.
Furthermore, the IEEE 48 standard mandates rigorous testing of busbar insulators for thermal and electrical performance. Research conducted by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) indicates that insulator failures can lead to costly outages and equipment damage, highlighting the need for compliance with these guidelines. Complying with these standards helps ensure that the insulators can handle the mechanical stresses and electrical loads characteristic of contemporary high-voltage systems. As industry demands evolve, maintaining adherence to these regulatory benchmarks will be critical for optimizing the lifespan and functionality of busbar insulators.
Busbar insulators play a crucial role in the stability and safety of modern electrical systems. Their primary function is to provide electrical insulation between busbars and their surrounding structures, preventing short circuits and ensuring reliable system performance. However, the failure of these insulators can have dire consequences. According to a report by the EPRI, insulator failure can lead to system outages that cost utilities upwards of $350,000 per hour in lost revenue and service disruptions.
Furthermore, data from the IEC indicates that approximately 40% of electrical system failures in substations are attributed to insulation breakdown. Such failures not only affect reliability but also pose significant safety risks to personnel and equipment. The implications of inadequate busbar insulation can extend beyond financial losses, with potential hazards including equipment damage, fire risks, and serious injury to electrical workers. Thus, investing in high-quality insulators and regular maintenance is essential to mitigate these risks and enhance the overall reliability of electrical systems.
The role of busbar insulators in modern electrical systems cannot be overstated, especially as industries demand greater efficiency and reliability in power distribution. Emerging materials, such as silicone rubber and composite polymers, are transforming the performance and longevity of busbar insulators. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global market for busbar systems is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5%, with advanced insulator technologies driving significant improvements in electrical safety and efficiency.
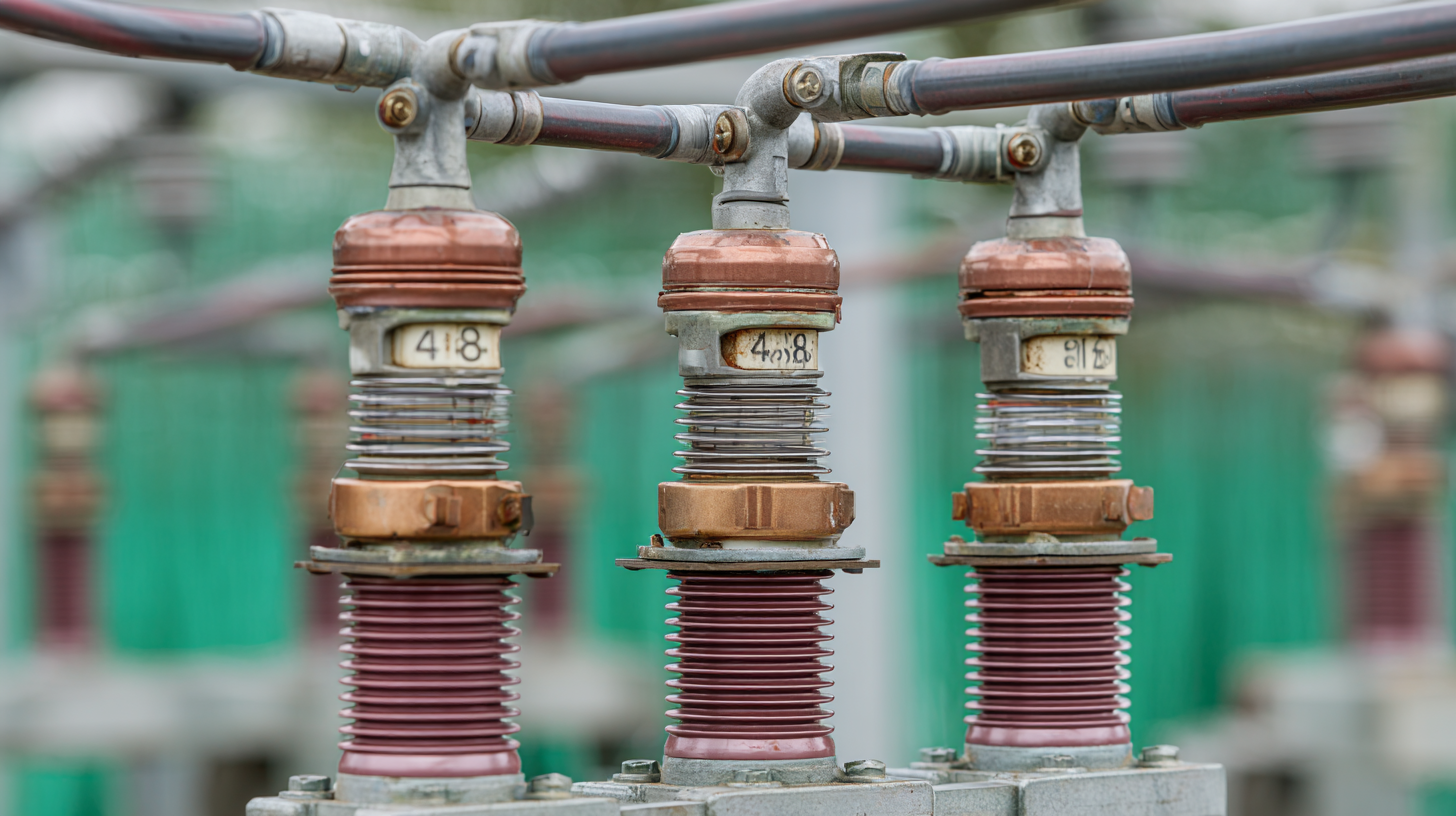
Incorporating advanced technologies like nanocomposites and automated manufacturing processes, engineers are now able to produce insulators that not only withstand higher voltage levels but also resist environmental degradation more effectively. A case study from the International Electrotechnical Commission indicates that the use of improved insulator materials can reduce failures by up to 40%, which is particularly critical in high-demand applications such as renewable energy systems. These innovations not only contribute to more resilient electrical grids but also align with the growing emphasis on sustainable energy solutions.